Understanding Interoperability in EMR Software
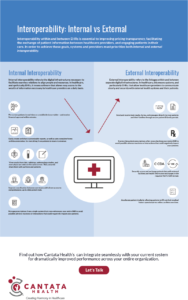
Interoperability is the ability to take different systems and software applications and help them utilize data seamlessly. In the context of EMR software, interoperability enables healthcare providers, hospitals, and other stakeholders to access and share patient information across different platforms.
Why We Need Interoperability in EMR Systems
Enhanced Patient Care
More often than not, patients are consulting multiple healthcare professionals for their various medical needs. Interoperability allows them all to access complete patient records. This comprehensive view enables better diagnosis, treatment planning, and coordinated care across multiple providers.
Streamlined Workflows
Interoperable EMR systems eliminate the need for manual data entry and information retrieval, reducing the risk of errors and saving valuable time for healthcare professionals. It enables automated exchange of data, such as lab results, radiology reports, and referrals, facilitating faster decision-making.
Continuity of Care
Interoperability promotes continuity of care by ensuring that patient data is accessible and up-to-date across different healthcare settings. This is especially crucial during transitions of care, such as referrals, hospital admissions, or transfers between healthcare facilities.
Improved Patient Engagement
Interoperable systems enable patients to access their health information securely, empowering them to actively participate in their care. It facilitates patient-provider communication, shared decision-making, and the ability to review and manage personal health records.
Current Challenges in Interoperability
Data Standardization
Different EMR systems may use varying data formats, coding schemes, and terminologies, making it difficult to interpret and exchange data accurately. Establishing standardized data formats, such as HL7, FHIR, and SNOMED CT, is crucial for effective interoperability.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Interoperability raises concerns regarding patient data privacy and security. Robust data encryption, access controls, and consent management mechanisms are vital to protect patient information during data exchange.
System Fragmentation
The presence of numerous EMR systems, each with its own proprietary standards and protocols, contributes to system fragmentation. This fragmentation hampers the smooth exchange of data and interoperability efforts.
Cost and Technical Challenges
Achieving interoperability requires significant investment in infrastructure, software customization, and integration efforts. Legacy systems, lack of IT resources, and technical complexities pose hurdles in achieving seamless interoperability.
Solutions for Seamless Interoperability
Adopting Interoperability Standards
Healthcare organizations and software vendors should adhere to widely accepted interoperability standards like HL7 and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR). These standards facilitate the uniform exchange of structured data and promote interoperability.
Implementation of APIs
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) play a crucial role in enabling data exchange between different software systems. By implementing robust APIs, EMR software can establish secure and standardized channels for sharing patient data.
Data Governance and Consent Management
Establishing comprehensive data governance policies, including data access controls and patient consent management frameworks, ensures that patient privacy is protected while enabling authorized data sharing.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Healthcare organizations, EMR vendors, and regulatory bodies should collaborate to develop and implement interoperability initiatives. Sharing best practices, lessons learned, and fostering partnerships can drive progress towards seamless data exchange.
Incentivizing Interoperability in EMR Systems
Governments and regulatory bodies can incentivize healthcare organizations and software vendors to prioritize interoperability. Offering financial incentives or imposing penalties for non-compliance can encourage stakeholders to invest in interoperability initiatives.
By adopting interoperability standards the healthcare industry can achieve the vision of seamless data exchange, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.