EMR software is great for every aspect of healthcare. Including medication prescribing. Among its many benefits, the most crucial is its ability to reduce medication errors, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. In this blog post, we will delve into how electronic medical records (EMR) software accomplishes this feat.
Understanding Medication Errors
Before delving into how EMR software mitigates medication errors, it’s essential to grasp the gravity of the issue. Medication errors are a prevalent concern in healthcare settings. They encompass a wide range of mistakes, including prescribing the wrong medication, administering an incorrect dosage, or overlooking potential drug interactions. These errors can have severe consequences, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications for patients.
EMR Software: A Pillar of Patient Safety
EMR software serves as a comprehensive digital repository for patient health records, replacing traditional paper-based systems. Beyond mere digitization, EMR systems offer a multitude of features designed to streamline healthcare processes and enhance patient safety. Let’s explore some ways in which EMR software helps to reduce medication errors:
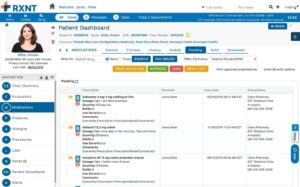
1. Accurate Prescribing Through EMR Software
One of the primary causes of medication errors is illegible handwriting on paper prescriptions, leading to misinterpretation by pharmacists. EMR software eliminates this issue by allowing healthcare providers to electronically prescribe medications directly from the patient’s record. This ensures clarity in prescription orders and enables real-time access to the patient’s medication history and potential allergies.
2. Decision Support Tools
EMR systems are equipped with sophisticated decision support tools. These provide healthcare professionals with real-time alerts and reminders regarding potential drug interactions, allergies, or contraindications. These prompts serve as a safety net, prompting providers to reconsider their prescribing decisions and take necessary precautions to prevent adverse events.
3. Comprehensive Patient Records
EMR software consolidates all aspects of a patient’s medical history into a single digital platform accessible to authorized healthcare professionals. This includes medication lists, dosage instructions, lab results, and past medical encounters. Having access to such comprehensive patient records ensures continuity of care and reduces the likelihood of duplicative or conflicting prescriptions.
4. Medication Reconciliation Through EMR Software
During transitions of care medication reconciliation becomes crucial to prevent discrepancies in a patient’s medication regimen. EMR software facilitates this process by automatically comparing the patient’s current medication list with previous prescriptions and flagging any inconsistencies. This ensures that healthcare providers have an accurate understanding of patient medication history, minimizing the risk of errors during transitions.
5. Remote Access and Collaboration
In today’s interconnected healthcare landscape, collaboration among providers across different specialties and settings is essential for delivering optimal care. EMR software enables seamless communication and information sharing among healthcare teams, regardless of geographical location. This facilitates timely consultations, reduces communication errors, and ensures that all providers involved are well-informed about their medication regimen.
The Impact of EMR Software on Patient Outcomes
The integration of EMR software into healthcare workflows has had a profound impact on patient outcomes, particularly concerning medication safety. By reducing the occurrence of medication errors, EMR systems contribute to:
- Improved Patient Satisfaction: Patients can have confidence that their medications are accurately prescribed and monitored, leading to greater trust in their healthcare providers.
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Minimizing medication errors reduces the risk of adverse drug reactions, hospital readmissions, and other complications. This ultimately promotes patient safety and well-being.
- Better Clinical Outcomes: With fewer medication errors, patients are more likely to experience positive treatment outcomes and faster recovery times, translating into overall improved health outcomes.